Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (46): 8116-8121.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.46.022
Previous Articles Next Articles
Stem cells in cartilage tissue engineering and influential factors
Wang Yan
- Department of Basic Medicine, School of Medical Instrument and Food Engineering, University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, Shanghai 200093, China
-
Online:2013-11-12Published:2013-11-30 -
About author:Wang Yan☆, Department of Basic Medicine, School of Medical Instrument and Food Engineering, University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, Shanghai 200093, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Yan. Stem cells in cartilage tissue engineering and influential factors[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(46): 8116-8121.
share this article
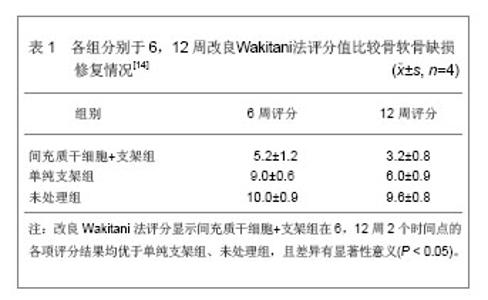
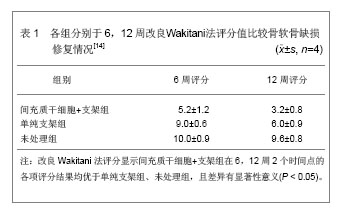
2.1 应用间充质干细胞构建组织工程化软骨 间充质干细胞来源于骨髓、骨膜、软骨膜、肌腱等处,具有多向分化潜能,在体外间充质干细胞需要诱导才能分化,根据诱导环境的不同,可以分化为软骨细胞或成骨细胞等。这种诱导包括添加不同的生长因子、分化因子、激素和细胞因子。间充质干细胞植入体内后,在新生组织上部形成透明软骨而在软骨下区则形成骨组织从而达到很好的界面整合。 间充质干细胞在组织工程化软骨动物实验中应用: 间充质细胞已经与各种支架材料联合应用,在动物实验研究中显示了良好的软骨修复潜能。王文良等[14]以骨髓间充质干细胞为种子细胞,运用纤维蛋白胶种植技术,以双层壳聚糖/羟基磷灰石复合支架为载体,修复骨软骨缺损,实验分3组,间充质干细胞+支架组为实验组,单纯支架组和未处理组为对照组。将修复材料植入到骨软骨缺损模型,分别于6,12周取材,采用Wakitani法对修复组织进行组织形态学评分[15],经统计学处理,各组修复效果差异有显著性意义 (P < 0.05),结果见表1。"
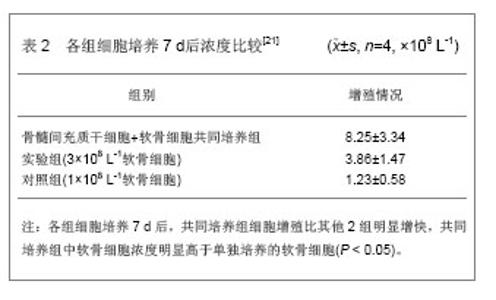
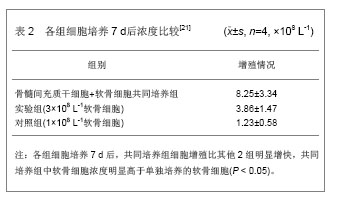
间充质干细胞在组织工程化软骨临床实验中应用:目前,有关间充质干细胞移植前是否需要诱导分化为软骨细胞尚存在一定的争议,应用间充质干细胞治疗人关节软骨缺损的临床实验很少。应用间充质干细胞作为种子细胞修复关节软骨缺损的临床研究最初由Wakitani等[16]进行了报道,其所采用的方法是将体外培养的自体骨髓间充质干细胞掺入Ⅰ型胶原凝胶后植入关节软骨缺损处,发现2周后植入处即有透明软骨的形成。 2002年,Wakitani等[17]报道了间充质干细胞的临床应用,对24例骨性关节炎患者进行临床实验。将经过体外扩增后与胶原凝胶结合的骨关节炎患者的骨髓穿刺液中分离纯化出自体骨髓间充质干细胞,移植到股骨内髁软骨缺损处,并覆盖以自体骨膜。结果植入后42周可见,缺损部位覆盖的软组织呈白色,在样本组织的几乎所有部位观察到甲苯胺蓝染色,观察到部分组织为透明软骨样组织形成。2007年,Wakitani等[18]获得了患者自体骨髓间充质干细胞,体外自体血清培养扩增并种植在胶原凝胶原膜上,植入软骨缺损部位,修复经关节镜证实的3个患者的髌骨关节软骨全层缺损,并用自体骨膜或滑膜覆盖,在植入6个月后患者的症状明显改善,而且保持17-27个月。 应用间充质干细胞构建组织工程化软骨的困难:在软骨组织工程中应用间充质干细胞的主要障碍是骨髓间充质干细胞表达多种表面标志物,目前还没有一个特异性的表面标志物[19-20]。因此,间充质干细胞的分离鉴定比较困难,在体外形成软骨过程中,间充质干细胞表达的透明软骨特异性标记物上调,Ⅱ型胶原和软骨特异性蛋白如蛋白聚糖,但是肥大软骨细胞的标记物如X型胶原和碱性磷酸酶也上调,构建的软骨组织不够成熟。而且取材困难,给患者带来的痛苦大,加之骨髓中的间充质干细胞含量非常少,上述不足限制了骨髓间充质干细胞的应用。 许多学者认为未经体外诱导软骨细胞的间充质干细胞在体内转化成软骨细胞的时间长,转化率低,所生成的软骨细胞数量较少,同时转化可能具有多向性,随机性。因此,认为如果在体外将间充质干细胞诱导为软骨细胞至一定的数量后再植入体内,将大大节省分化时间,并显著提高分化效率。谢鹏等[21]探讨自体骨髓间充质干细胞和同种异体软骨细胞共培养优化软骨组织工程种子的细胞源的可行性。使用密度梯度离心和贴壁筛选的方法获得骨髓间充质干细胞,取细胞浓度为3×108 L-1的第2代骨髓间充质干细胞和软骨细胞,随机分为3组。共培养组:将骨髓间充质干细胞和软骨细胞按2∶1比例混匀;实验组:取同代同浓度的软骨细胞(浓度与共培养细胞的终浓度相同);对照组:取低浓度软骨细胞1×108 L-1 (与共培养组中软骨细胞终浓度相同)。各组培养7 d后浓度比较,结果见表2。 结果显示,自体骨髓间充质干细胞与同种异体软骨细胞共培养未见明显排异反应,提示自体骨髓间充质干细胞与同种异体软骨细胞为种子细胞共培养,骨髓间充质干细胞能促进软骨细胞的增殖和细胞外基质合成,缩短软骨细胞培养时间和减少传代次数,同时软骨细胞可促进骨髓间充质干细胞向软骨细胞的定向转化,节省大量软骨细胞。 2.2 应用脂肪干细胞构建组织工程化软骨 脂肪来源干细胞与骨髓间充质干细胞一样均属于来自中胚层的成体干细胞,因此具有较为相似的生物学特性。2001年4月,Zuk等[22]发现从患者臀部和大腿处脂肪抽吸物中存在含有大量多项分化潜能的类似干细胞的细胞,这些细胞可以发育成健康的软骨和肌肉等。首次从脂肪组织中发现干细胞,并首次命名为脂肪干细胞。随后更多的实验发现脂肪干细胞可向软骨细胞、骨细胞及脂肪细胞等多种细胞分化,脂肪干细胞贴壁能力强,对培养基的营养需求低,对血清无特殊选择性,体外易于培养,体外倍增速度快于骨髓间充质干细胞,而且传代过程中,细胞增殖能力稳定。另外脂肪干细胞来源于脂肪组织,来源广,含量丰富,其中脂肪干细胞的获取率大约为1/1 000,是骨髓基质干细胞获取率的100倍[23]。并且提取过程简单,创伤小,因此,有望成为理想的种子细胞。 相关实验已证实脂肪干细胞能够向中胚层细胞系包括脂肪、软骨、骨、肌肉和其他胚层细胞系包括神经、内皮等转化[24]。近年来,研究者利用脂肪干细胞在体内外成功构建了组织工程软骨,使之成为了软骨组织工程领域又一理想的种子细胞[25]。关于把脂肪干细胞移植到体内之前是否需要体外诱导存在争议。一些研究者认为体外诱导时间长,价格昂贵不需要体外诱导,而另一部分研究者认为不经体外诱导直接移植到体内的脂肪干细胞成骨化比较慢甚至不出现,因此体外诱导是必须的。 伍耀豪等[26]分析了自体脂肪干细胞修复猪关节软骨缺损的可行性。从猪背部脂肪组织中获取脂肪干细胞,经过体外培养扩增,以50×109 L-1L的细胞浓度将脂肪干细胞接种于聚乳酸聚乙醇酸共聚物中,细胞材料复合物在体外成软骨诱导2周。于猪膝关节软骨非负重区形成2个直径8 mm的环形、全层软骨缺损,实验组回植经诱导后的细胞材料复合物,对照组放置单纯支架材料。术后12周取材,缺损修复区行大体观察、组织学苏木精-伊红染色及藏红花染色、免疫组化检测。结果发现术后12周实验组缺损区大部分被修复,缺损被软骨组织填充,修复区表面光滑,组织学染色显示有典型的透明软骨样结构,藏红花染色发现修复组织表达丰富的聚合蛋白多糖,对照组则未能修复关节软骨缺损,缺损区面积增大,表面覆盖薄层纤维组织,因此,认为猪自体脂肪干细胞可以作为组织工程种子细胞,修复猪关节软骨缺损。 De等[27]认为,脂肪干细胞与骨髓间充质干细胞相比,两者在生长动力学、细胞凋亡和向成骨细胞分化上差异均无显著性意义,两者转染慢病毒和逆转录病毒的效率相似,骨髓干细胞的扩增效率较骨髓来源的干细胞高,培养方便,在第14,15代时仍未出现细胞老化现象。同时Im等[28]认为,尽管这些结果还需要进一步的研究,包括体内移植和诱导因子的重选择,但脂肪干细胞成软骨潜能可能要弱于骨髓间充质干细胞,脂肪组织作为干细胞来源,尚须进一步的研究。 2.3 应用胚胎干细胞构建组织工程化软骨 胚胎干细胞是胚胎发育早期胚泡内细胞团中未分化的细胞,它具有发育全能性,理论上能分化为包括生殖细胞在内的成体的所有组织和器官。理论上,任何涉及正常细胞缺乏的疾病都可由移植胚胎干细胞分化而来的相应组织治疗。1998年,Thomson等[29]从体外人工受精的内细胞团分离获得人胚胎干细胞。在此基础上,2000年,澳大利亚和新加坡科学家合作,成功的从人囊胚中建立了人胚胎干细胞体系[30]。人胚胎干细胞具有以下特点:①在特定条件下,可以在体外增殖并保持未分化状态,具有全能性和形成嵌合体动物的能力。②具有正常的二倍体核型及高水平的端粒酶活性。③表达原始胚胎干细胞表面抗原。④具有受精卵的某些特性,保持向滋养层细胞及三胚层来源的所有细胞分化的潜能,可多向分化,无限增殖,可以分化成胎儿和成体内各种类型的组织细胞。⑤能够常规冻存和复苏,长期培养并保持高度未分化状态和发育潜能性。 虽然这些胚胎干细胞研究尚处于早期实验阶段,然而在过去的数年中,依靠调整小鼠胚胎干细胞的生长环境,产生分化的特殊细胞已成为现实。2006年,Hwang等[31]通过研究发现,胚胎干细胞在聚乙二醇水凝胶作支架的三维环境中培养,明显优于单层培养,在体外软骨培养基中培养第17天时,作基因表达和相关的蛋白分析,软骨相关的标志物明显上调。然而组织工程化软骨研究中,对胚胎干细胞的研究开展相对较晚。尽管胚胎干细胞的增殖能力较强,但对其选择纯化较为困难,且胚胎干细胞具有致瘤性。临床使用尚存在伦理学问题。 2.4 软骨组织工程种子细胞的影响因素 生长因子:干细胞作为组织工程化软骨的种子细胞,其生长、繁殖、代谢是极其复杂的,受诸多因素影响。细胞因子是其中一种。生长因子是细胞因子的一大分类,对软骨细胞生长、繁殖起着重要作用。不同的生长因子相互影响、相互协同共同作用于干细 胞[32]。转化生长因子β是一簇具有多种功能的蛋白多肽,体内能发挥多种生物学效应。胰岛素样生长因子是一簇依赖生长激素的多肽蛋白质。碱性成纤维细胞生长因子是目前已知最强的促细胞生长因子。作为关节软骨的有丝分裂原,它促进软骨细胞增殖并使增殖细胞稳定的向成熟软骨细胞分化[33]。 细胞支架:细胞支架作为软骨组织工程的三维构架,不仅提供软骨细胞生长依附的框架,使之形成特定的组织或器官,更重要的是细胞支架作为细胞外基质成分之一,起着介导细胞间信号传递和相互作用的媒介作用。细胞支架是软骨组织工程中细胞生长的主要环境,对软骨的生长具有重要影响作用。周强等[34]联合应用自制生物凝胶和三维支架材料,建立组织工程种子细胞的三维支架双相接种技术,并对其构建生成组织工程关节软骨的效果进行初步观察。结果发现,随着培养时间的延长,软骨组织的形成是由外周向中心进行,培养2周后,逐渐形成富含Ⅱ型胶原和蛋白聚糖、具有典型软骨组织结构的成熟工程化软骨。同时,Ⅰ型胶原逐渐转为阴性,支架材料亦不断降解,4周时,硫酸糖胺多糖含量平均为(15.70± 2.00) mg/g(湿质量),为天然关节软骨的30%以上,因此认为种子细胞的三维支架双相接种技术简便易行,不仅实现了种子细胞与支架材料的高效复合,而且能保持种子细胞在支架材料中稳定的三维均相分布,促进了工程化关节软骨组织的形成和成熟。 细胞的接种密度:细胞的密度不仅影响相对接种存活率、生长速度,还与软骨细胞表型表达密切相关。大量实验证明,接种的软骨细胞密度大,细胞相对生长较好。戴刚等[35]为优化关节软骨组织工程种子细胞的体外获取方法。分析不同代次体外单层培养幼兔关节软骨细胞接种密度与相对接种存活率的关系,并观察其细胞生长状况、形态特征及分化功能。结果发现,相同培养条件下,体外单层培养关节软骨细胞的相对接种存活率和生长活性与其接种密度呈正相关;同一代次适宜密度(2.0-3.0)×104/cm2接种者的相对接种存活率和生长活性同高密度(4.0-5.0)×104/cm2接种者相近;传代培养(第2-4代)细胞的相对接种存活率和生长活性相对高于原代培养者。因此,在相同培养条件下及一定传代次数内,适宜密度接种进行关节软骨细胞单层传代培养,可获取数量多、活性高的关节软骨组织工程种子细胞。 氧浓度:氧浓度对软骨细胞和胶原的合成有明显影响。氧浓度过高、过低都不利于软骨细胞生长、繁殖及代谢。O’Driscoll等[36]实验研究证明,氧体积分数为12%-25%时软骨细胞生长及代谢最佳,在>90%、<5%时,细胞生长受抑制,分泌基质减少。 应力和微重力:机体的软骨细胞都处于动力微环境中生长的。功能负荷或肌肉牵张力使软骨细胞生长在动力微环境中。动力微环境有利于软骨细胞的生长、繁殖及代谢。Vunjak-Novakovic等[37]实验中发现,软骨细胞在张应力环境下进行培养,所产生的细胞外基质更多,并具有良好生物学特性。在力学环境中,软骨细胞或组织受力后通过基质将受力信号传递给软骨细胞,软骨细胞以信号来调节基质的成分。力学刺激对调控软骨细胞代谢及维持细胞外基质正常表达起重要作用。 其他相关因素:理想的组织工程软骨要有适当的细胞和细胞外基质比例,同时还有好的力学性能。这需要延长体外培养时间,以满足上述要求。生物反应器是一个良好的选择,它能够提高细胞活性和成软骨能力。常用的生物反应器有旋转瓶式、灌注式、旋转壁式、流体静压系统等,结合三维立体支架,能够显著提高组织工程软骨的生物力学性质和生物化学功能。 "
| [1]李丽霞,王丽,王正辉,等.同种异体软骨移植免疫排斥反应的研究进展[J].中国美容医学,2008,17(3):452-454. [2]文昌明,王洪,杨述华,等.同种异体骨软骨柱移植治疗关节软骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(31):6050-6054. [3]Landis WJ,Jacquet R,Hillyer J,et al.The potential of tissue engineering in orthopedics.Orthop Clin North Am.2005; 36(1):97-104. [4]Vats A,Tolley NS,Polak JM,et al.Stem cells: sources and applications.Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci.2002;27(4):227-232. [5]Saadeh PB,Brent B,Mehrara BJ,et al.Human cartilage engineering: chondrocyte extraction, proliferation, and characterization for construct development.Ann Plast Surg. 1999;42(5):509-513. [6]Redman SN,Oldfield SF,Archer CW.Current strategies for articular cartilage repair.Eur Cell Mater.2005;14(9):23-32. [7]Kino-oka M,Maeda Y,Ota Y,et al.Process design of chondrocyte cultures with monolayer growth for cell expansion and subsequent three-dimensional growth for production of cultured cartilage.J Biosci Bioeng.2005; 100(1): 67-76. [8]Hegert C,Kramer J,Hargus G,et al.Differentiation plasticity of chondrocytes derived from mouse embryonic stem cells.J Cell Sci.2002;115(23):4617-4628. [9]Wakitani S,Kimura T,Hirooka A,et al.Repair of rabbit articular surfaces with allograft chondrocytes embedded in collagen gel.J Bone Joint Surg Br.1989;71(1):74-80. [10]Cao Y,Vacanti JP,Paige KT,et al.Transplantation of chondrocytes utilizing a polymer-cell construct to produce tissue-engineered cartilage in the shape of a human ear.Plast Reconstr Surg.1997;100(2):297-302. [11]Johnstone B,Hering TM,Caplan AI,et al.In vitro chondrogenesis of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal progenitor cells.Exp Cell Res.1998;238(1):265-272. [12]中国知网.中国学术期刊总库[DB/OL].2013-8-10. https://www.cnki.net [13]SCI数据库.Web of Sciencevia ISI Web of Knowledge[DB/OL]. 2013-8-15.http://ip-science.thomsonreuters.com/mjl [14]王文良,张华亮,关静,等.壳聚糖/羟基磷灰石支架修复骨软骨缺损的实验研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2008,16(20):1579-1583. [15]Urist MR,Strates BS.Bone formation in implants of partially and wholly demineralized bone matrix.Including observations on acetone-fixed intra and extracellular proteins.Clin Orthop Relat Res.1970;71:271-278. [16]Wakitani S,Goto T,Pineda SJ,et al.Mesenchymal cell-based repair of large, full-thickness defects of articular cartilage.J Bone Joint Surg Am.1994;76(4):579-592. [17]Wakitani S,Imoto K,Yamamoto T,et al.Human autologous culture expanded bone marrow mesenchymal cell transplantation for repair of cartilage defects in osteoarthritic knees.Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2002;10(3):199-206. [18]Wakitani S,Nawata M,Tensho K,et al.Repair of articular cartilage defects in the patello-femoral joint with autologous bone marrow mesenchymal cell transplantation: three case reports involving nine defects in five knees.J Tissue Eng Regen Med.2007;1(1):74-79. [19]张翼,宋敬锋,白俊清.骨髓间充质干细胞研究进展及在软骨组织工程中的应用[J].中国煤炭工业医学杂志,2007,10(1):1-3. [20]曹华,周红辉,吴剑.骨髓间充质干细胞及在软骨组织工程中的研究进展[J].中国现代医生,2008,46(24):53-55. [21]谢鹏,张仲文.自体骨髓间充质干细胞和同种异体软骨细胞共培养优化软骨组织工程种子的细胞源[J].中国组织工程研究,2012, 16(14):2509-2514. [22]Zuk PA,Zhu M,Mizuno H,et al.Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: implications for cell-based therapies.Tissue Eng.2001;7(2):211-228. [23]Zuk PA,Zhu M,Ashjian P,et al.Human adipose tissue is a source of multipotent stem cells.Mol Biol Cell.2002;13(12): 4279-4295. [24]Guilak F,Lott KE,Awad HA,et al.Clonal analysis of the differentiation potential of human adipose-derived adult stem cells.J Cell Physiol.2006;206(1):229-237. [25]Mochizuki T,Muneta T,Sakaguchi Y,et al.Higher chondrogenic potential of fibrous synovium- and adipose synovium-derived cells compared with subcutaneous fat-derived cells: distinguishing properties of mesenchymal stem cells in humans. Arthritis Rheum.2006;54(3):843-853. [26]伍耀豪,刘广鹏,刘波,等.应用自体脂肪干细胞修复猪关节软骨缺损的初步实验研究[J].组织工程与重建外科杂志,2006,2(3): 163-166. [27]De Ugarte DA,Morizono K,Elbarbary A,et al.Comparison of multi-lineage cells from human adipose tissue and bone marrow.Cells Tissues Organs.2003;174(3):101-109. [28]Im GI,Shin YW,Lee KB.Do adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells have the same osteogenic and chondrogenic potential as bone marrow-derived cells?Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2005;13(10):845-853. [29]Thomson JA,Itskovitz-Eldor J,Shapiro SS,et al.Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts.Science. 1998;282(5391):1145-1147. [30]Reubinoff BE,Pera MF,Fong CY,et al.Embryonic stem cell lines from human blastocysts: somatic differentiation in vitro.Nat Biotechnol.2000;18(4):399-404. [31]Hwang NS,Kim MS,Sampattavanich S,et al.Effects of three-dimensional culture and growth factors on the chondrogenic differentiation of murine embryonic stem cells.Stem Cells.2006;24(2):284-291. [32]李想,王以朋,洪毅,等.碱性成纤维细胞生长因子对人椎间盘细胞外基质合成及软骨调节素表达的影响[J].中国康复理论与实践, 2012,18(6):539-543. [33]赵宇,孙立伟,姜锐,等.碱性成纤维细胞生长因子修复功能及其应用研究进展[J].中国老年学杂志,2012,32(11):2418-2420. [34]周强,李起鸿,戴刚,等.关节软骨细胞三维支架双相接种体外生成软骨组织的观察[J].中华骨科杂志,2002,22(6):372-376. [35]戴刚,李起鸿,周强,等.关节软骨组织工程种子细胞的优化获取[J].第三军医大学学报,2002,24(2):129-131. [36]O'Driscoll SW,Fitzsimmons JS,Commisso CN.Role of oxygen tension during cartilage formation by periosteum.J Orthop Res.1997;15(5):682-687. [37]Vunjak-Novakovic G,Martin I,Obradovic B,et al.Bioreactor cultivation conditions modulate the composition and mechanical properties of tissue-engineered cartilage.J Orthop Res.1999;17(1):130-138. |
| [1] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [2] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [3] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [4] | Hui Xiaoshan, Bai Jing, Zhou Siyuan, Wang Jie, Zhang Jinsheng, He Qingyong, Meng Peipei. Theoretical mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine theory on stem cell induced differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1125-1129. |
| [5] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [6] | Fan Yiming, Liu Fangyu, Zhang Hongyu, Li Shuai, Wang Yansong. Serial questions about endogenous neural stem cell response in the ependymal zone after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1137-1142. |
| [7] | Tian Chuan, Zhu Xiangqing, Yang Zailing, Yan Donghai, Li Ye, Wang Yanying, Yang Yukun, He Jie, Lü Guanke, Cai Xuemin, Shu Liping, He Zhixu, Pan Xinghua. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulate ovarian aging in macaques [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 985-991. |
| [8] | Hou Jingying, Guo Tianzhu, Yu Menglei, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning targets and downregulates miR-195 and promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell survival and pro-angiogenic potential by activating MALAT1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1005-1011. |
| [9] | Zhou Ying, Zhang Huan, Liao Song, Hu Fanqi, Yi Jing, Liu Yubin, Jin Jide. Immunomodulatory effects of deferoxamine and interferon gamma on human dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1012-1019. |
| [10] | Liang Xuezhen, Yang Xi, Li Jiacheng, Luo Di, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Bushen Huoxue capsule regulates osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via Hedgehog signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1020-1026. |
| [11] | Wang Jifang, Bao Zhen, Qiao Yahong. miR-206 regulates EVI1 gene expression and cell biological behavior in stem cells of small cell lung cancer [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1027-1031. |
| [12] | Liu Feng, Peng Yuhuan, Luo Liangping, Wu Benqing. Plant-derived basic fibroblast growth factor maintains the growth and differentiation of human embryonic stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1032-1037. |
| [13] | Wen Dandan, Li Qiang, Shen Caiqi, Ji Zhe, Jin Peisheng. Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton for extemal use improves the viability of adipogenic mesenchymal stem cells and promotes diabetes wound repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1038-1044. |
| [14] | Zhu Bingbing, Deng Jianghua, Chen Jingjing, Mu Xiaoling. Interleukin-8 receptor enhances the migration and adhesion of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to injured endothelium [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1045-1050. |
| [15] | Luo Xiaoling, Zhang Li, Yang Maohua, Xu Jie, Xu Xiaomei. Effect of naringenin on osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1051-1056. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||